Introduction
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) infections of the larynx are exceedingly rare, yet they present significant challenges, particularly in stroke patients. The research article titled Herpes simplex laryngitis presenting as airway obstruction in a stroke patient??? provides valuable insights into this uncommon condition. This blog aims to explore how speech-language pathologists (SLPs) can leverage these findings to improve patient outcomes and encourage further research in this area.
Case Study Overview
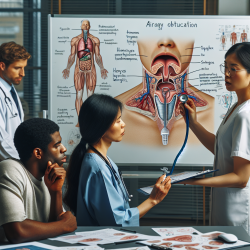
The study details the case of a 55-year-old woman with a history of stroke who developed HSV laryngitis, leading to airway obstruction. The patient exhibited symptoms such as stridor and dysphagia, complicating her recovery. The diagnosis was confirmed through laryngoscopy and biopsy, revealing ulcerative herpes laryngitis.
Despite the rarity of HSV laryngitis, early diagnosis and treatment are crucial. The patient responded well to antiviral therapy, underscoring the importance of prompt intervention.
Implications for Speech-Language Pathologists
For SLPs, this case highlights several critical considerations:
- Early Detection: SLPs should maintain a high index of suspicion for HSV laryngitis in stroke patients presenting with airway issues. Early detection can significantly improve management and outcomes.
- Comprehensive Evaluation: Given the overlap of symptoms between neurological and laryngeal conditions, a thorough evaluation is essential. SLPs should collaborate with otolaryngologists to ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment.
- Interdisciplinary Approach: Managing HSV laryngitis requires a team approach. SLPs should work closely with medical professionals to address both the laryngeal and neurological aspects of care.
Encouraging Further Research
The rarity of HSV laryngitis, particularly in stroke patients, presents an opportunity for further research. SLPs can play a vital role in advancing knowledge in this area by:
- Documenting Cases: SLPs should document and share cases of HSV laryngitis to build a more comprehensive understanding of its presentation and management.
- Collaborative Research: Partnering with medical researchers to explore the pathophysiology and treatment of HSV laryngitis can lead to improved therapeutic strategies.
- Exploring Pediatric Implications: While this case focuses on adults, understanding HSV laryngitis in children could offer insights into developmental and anatomical factors influencing the condition.
Conclusion
Herpes simplex laryngitis in stroke patients is a complex condition that requires careful consideration and management. By applying the insights from this case study, SLPs can enhance their practice and contribute to the broader understanding of this rare condition. Early diagnosis, interdisciplinary collaboration, and ongoing research are key to improving outcomes for affected patients.
To read the original research paper, please follow this link: Herpes simplex laryngitis presenting as airway obstruction in a stroke patient???