Introduction
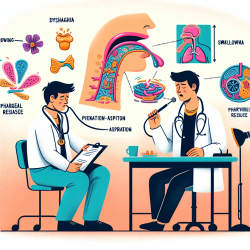
As practitioners in the field of speech-language pathology, it is crucial to base our clinical decisions on evidence-based research. The study titled "The Risk of Penetration–Aspiration Related to Residue in the Pharynx" offers valuable insights into the relationship between pharyngeal residue and the risk of penetration-aspiration, a common concern in dysphagia management. Understanding these findings can significantly enhance clinical outcomes for children and adults with swallowing disorders.
Key Findings from the Study
The research analyzed data from 305 adults at risk for dysphagia, focusing on the presence of pharyngeal residue and its impact on penetration-aspiration during swallowing. The study identified that a pharyngeal residue threshold of 1% is a critical point for increased risk of penetration-aspiration. Specifically, the odds of penetration-aspiration increased 4.60-fold for thin liquids and 2.11-fold for mildly thick liquids when residue exceeded this threshold.
Implications for Clinical Practice
For practitioners, these findings underscore the importance of assessing pharyngeal residue during swallowing evaluations. Implementing strategies to minimize residue can reduce the risk of penetration-aspiration, thereby improving patient safety and outcomes. Consider the following approaches:
- Regular Assessment: Incorporate videofluoroscopic swallow studies to monitor residue levels and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
- Consistency Modifications: Tailor the consistency of liquids and foods to reduce residue and enhance swallowing safety.
- Therapeutic Exercises: Implement exercises that strengthen pharyngeal muscles and improve bolus clearance.
Encouraging Further Research
While this study provides significant insights, it also highlights the need for further research. Understanding the mechanisms behind residue formation and its impact on different consistencies can lead to more targeted interventions. Practitioners are encouraged to engage in research activities or collaborate with academic institutions to expand the knowledge base in this area.
Conclusion
The study "The Risk of Penetration–Aspiration Related to Residue in the Pharynx" provides critical data that can guide clinical practices in managing dysphagia. By focusing on reducing pharyngeal residue, practitioners can significantly decrease the risk of penetration-aspiration and improve patient outcomes. For those interested in delving deeper into the research, The Risk of Penetration–Aspiration Related to Residue in the Pharynx offers comprehensive insights.